Photo © 2011 UNICEF/ Shehzad Noorani
Using a large flip chart, a female health worker gives health education to a group of pregnant women while they wait for service in a UNICEF supported MCH clinic (Maternal and Child) in the city of Musanze in northern Rwanda.
Home > Country action > Rwanda
Download the full profile with additional key demographics, progress against milestones, and more.
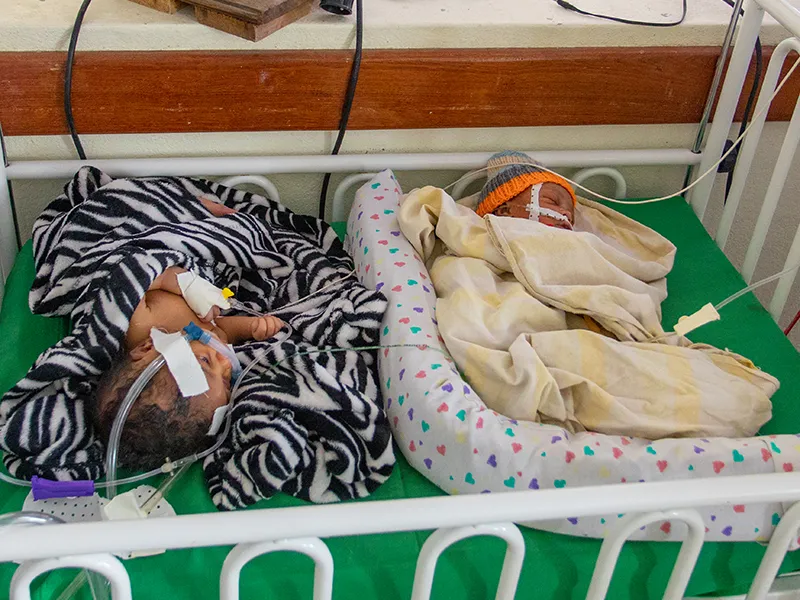
Photo © 2020 UNICEF/ Isaac Rudakubana
Two newborns rest in the neonatal ward of Rubavu Hospital, Rwanda.
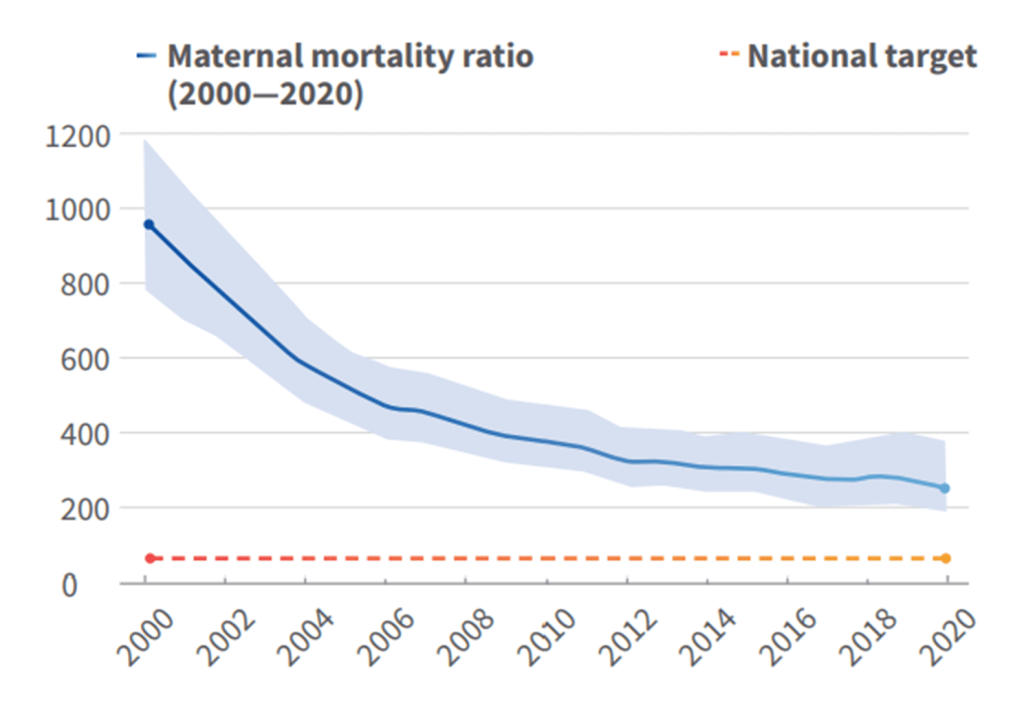
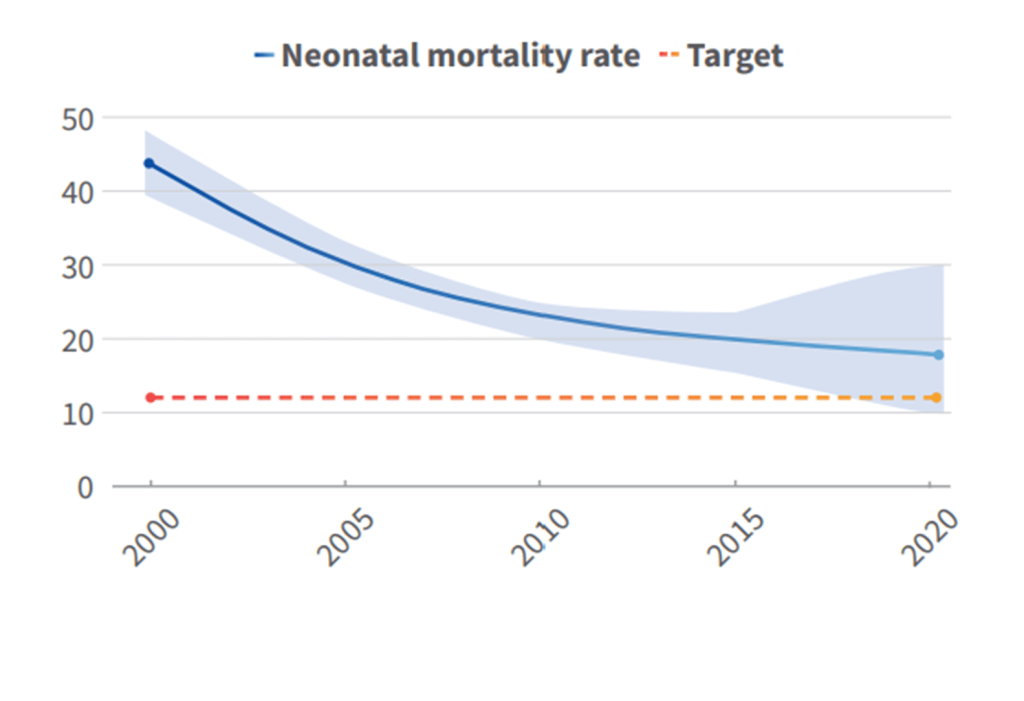
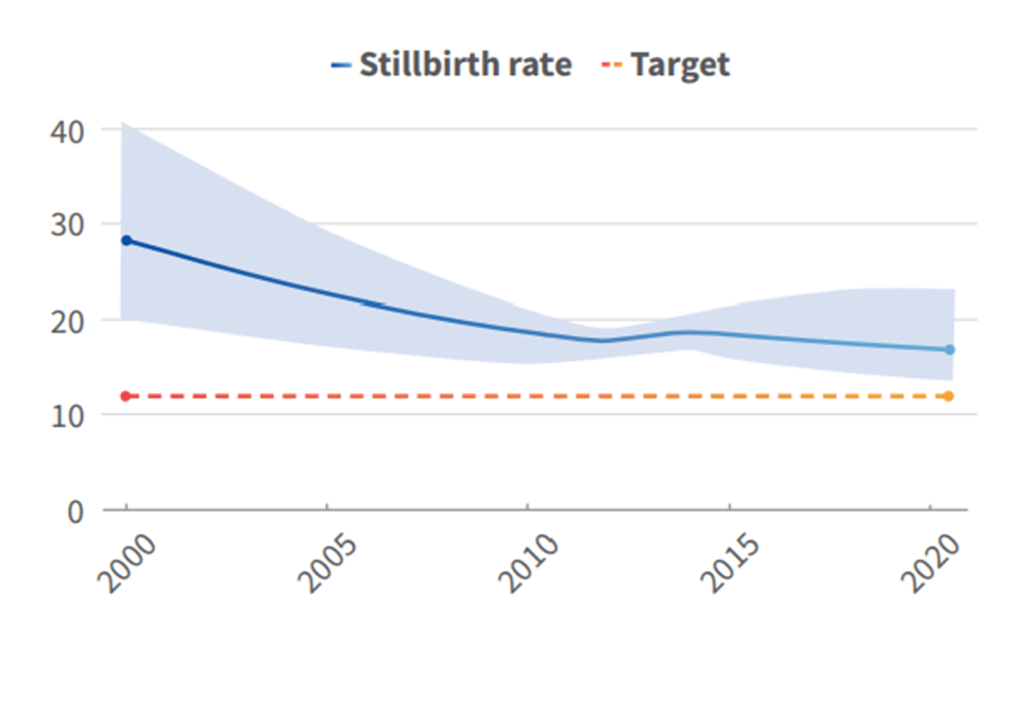
Photo © 2020 UNICEF/ Isaac Rudakubana
A mother in Rubavu Hospital, Rwanda practices ‘kangaroo care’ to keep her prematurely born baby warm and regulate body temperature.
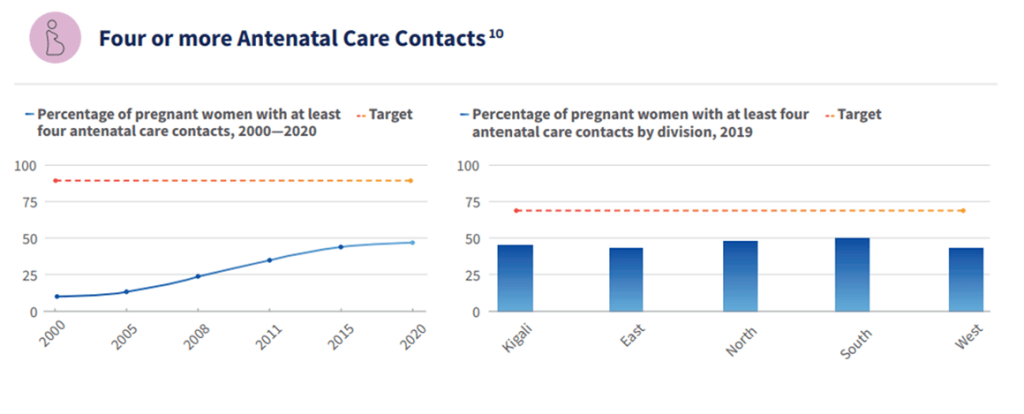
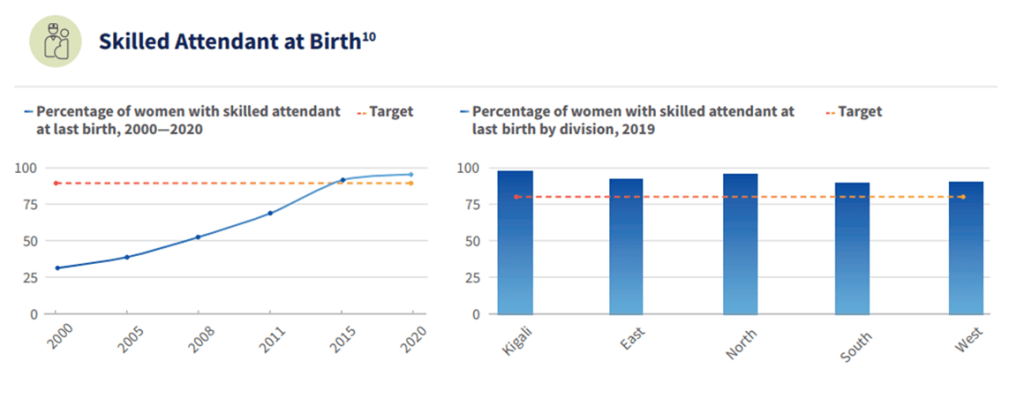
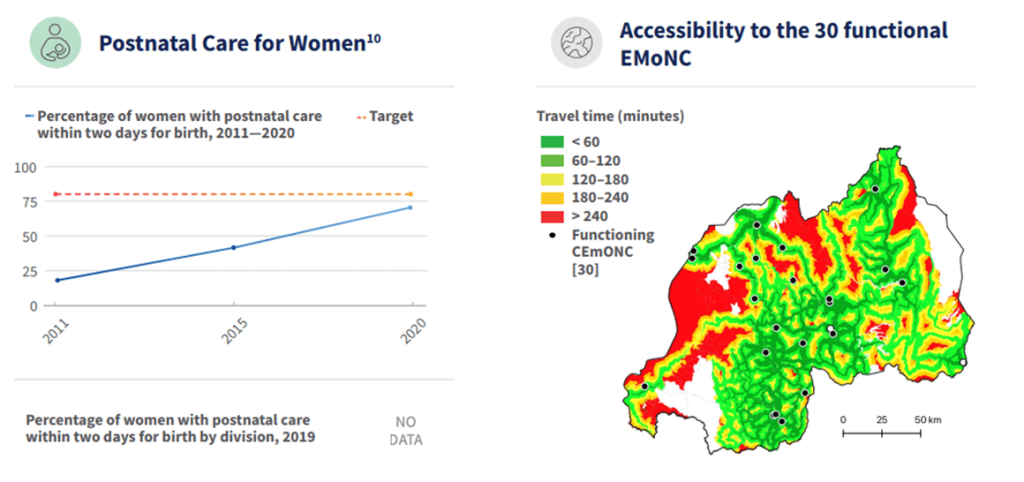
Photo © 2016 UNICEF/ Habib Kanobana
Jyamima Nyirahabimana recently gave birth to twins. Both babies were born premature, but Jyamima is not worried. She is being taught “Kangaroo Mother Care”, which promotes growth and regulates body temperature through skin-to-skin contact between her and the babies.
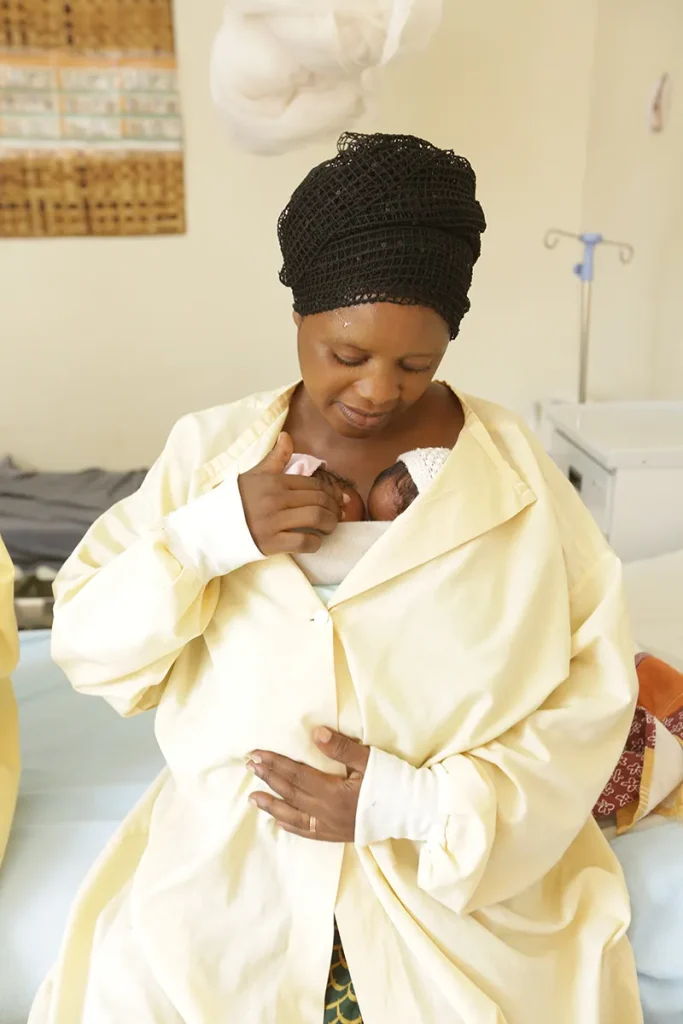

Photo © 2016 UNICEF/ Habib Kanobana
Jyamima Nyirahabimana holds her twin babies close to her body. Although both babies were born premature, but Jyamima is not worried. She has been taught the “Kangaroo Care”, which promotes growth, regulates body temperature, and encourages deeper sleep through skin-to-skin contact between her and the babies.
Rwanda’s successes in improving quality of care for maternal, newborn and child health are essential to help reduce maternal and newborn mortality and stillbirths. These include:
Photo © 2020 WHO / Tatiana Almeida
Midwives during WHO Head of Sub-Office Dr Kai von Harbou visit to Hope Field Hospital
©EWENE 2024 | Privacy Policy | Website by Blick Creative
Photo © 2020 WHO / Tatiana Almeida
Midwives during WHO Head of Sub-Office Dr Kai von Harbou visit to Hope Field Hospital
© 2024 ENAP EPMM | Privacy Policy | Website by Blick Creative